Expert Inguinal Hernia
What is an Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia occurs when a part of the intestine or abdominal tissue pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, causing a bulge or lump in the groin area. This happens usually while lifting a heavy object, coughing or bending over. This type of hernia mostly affects males. Hence, if you are suffering from this hernia, seek medical attention from an inguinal hernia laparoscopic surgeon.
Types of Inguinal Hernia

Direct inguinal hernia
This kind of inguinal hernia mainly affects older men. It is characterised by protrusion of the contents of the abdomen through the wall of the inguinal canal. Direct inguinal hernias are usually less common than indirect inguinal hernias.
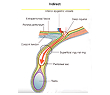
Indirect inguinal hernia
When the abdominal contents like a part of the intestine protrudes into the inguinal canal, it results in an indirect inguinal hernia. This type of hernia is mainly congenital (present at the time of birth). In some cases, it may also affect young adults due to activities such as straining or heavy lifting.
Types of Inguinal Hernia

Direct inguinal hernia
This kind of inguinal hernia mainly affects older men. It is characterised by protrusion of the contents of the abdomen through the wall of the inguinal canal. Direct inguinal hernias are usually less common than indirect inguinal hernias.

Indirect inguinal hernia
When the abdominal contents like a part of the intestine protrudes into the inguinal canal, it results in an indirect inguinal hernia. This type of hernia is mainly congenital (present at the time of birth). In some cases, it may also affect young adults due to activities such as straining or heavy lifting.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, a patient's family history can affect the diagnosis process of inguinal hernia. This information can help doctors assess risk factors and guide their diagnosis.
Inguinal hernia in females causes pain in the groin area, similar to males. It may also radiate to the lower abdomen or pelvis. Women may experience discomfort during physical activities, coughing, or straining.
Pain in the inguinal region of males is often caused by a hernia, which can lead to pressure on surrounding tissues. This is one of the common symptoms of inguinal hernia in males.
Recovery time after inguinal hernia surgery varies but generally ranges from a few days to several weeks. Laparoscopic surgery usually allows for a quicker recovery, with many patients returning to light activities within a week. Full recovery may take up to 4 to 6 weeks.
A congenital inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weakness in the abdominal wall, often due to incomplete closure of the inguinal canal during foetal development. This type of hernia is present at birth and is more common in males.
Surgery is the primary and most effective treatment for inguinal hernias, especially when symptoms are present. It is recommended to prevent potential complications, such as incarceration or strangulation.
The minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic inguinal hernia surgery often makes it the safer option as it results in lesser pain, shorter recovery time, and lower rates of infection compared to open surgery.
Indirect inguinal hernia surgery usually lasts about 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the complexity of the case and the surgical method used (open or laparoscopic).
Symptoms of Inguinal Hernia
Inguinal hernia symptoms are listed down below.
- A bulge in the area on either side of the pubic bone
- An aching or burning sensation near the site of the bulge
- Pain or discomfort in the groin
- Swelling and pain around the testicles
If you notice any of the aforementioned symptoms, consult Dactar Babu to determine if you need to undergo inguinal hernia laparoscopic surgery.
Causes of Inguinal Hernia
Some of the most common causes of inguinal hernia have been mentioned below.
Age:
As the connective tissues start to weaken with advancing age, the risk of developing inguinal hernia increases.
Gender:
Males are more prone to suffer from inguinal hernias than females. This is due to their natural body structure, especially that of the inguinal canal.
Family history:
Some individuals with a family history of hernia are at a higher risk.
Obesity:
Excess body weight can cause the abdominal muscles to weaken and result in the development of inguinal hernia.
Congenital factors:
Weakness in the abdominal wall present from birth can lead to inguinal hernia.
Chronic cough or straining:
Conditions that lead to persistent straining or coughing such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or constipation can cause inguinal hernia.
Heavy lifting:
Regularly engaging in heavy lifting can strain the abdominal muscles and increase hernia risk.
Diagnosis of Inguinal Hernia
The diagnosis of an inguinal hernia usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, as well as diagnostic tests. During the physical exam, the inguinal hernia doctors will check the hernia by attempting to see or feel it. They may ask you to cough or strain (as if having a bowel movement) to check for any lump or bulge. If the hernia is not easily visible, additional tests may be used to detect it internally. Common diagnostic tests include:
Ultrasound:
A non-invasive imaging technique that can confirm the presence of an inguinal hernia, its location, and the size of the hernia sac.
CT Scan:
A computed tomography scan offers detailed images of the abdominal area, useful for diagnosing and evaluating the hernia’s size.
MRI:
Magnetic resonance imaging offers clear, detailed images that may be used in certain cases to confirm the diagnosis of an inguinal hernia.
Blood Tests:
These may be done to check for infection or inflammation.
If you suspect an inguinal hernia or experience symptoms like groin discomfort or a bulge, consult a doctor for inguinal hernia treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment, including possible surgery, are essential to prevent complications.
Inguinal Hernia Treatments
Surgical Treatment for Inguinal Hernia
There are two primary methods for repairing an inguinal hernia:
1. Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Surgery:
In this traditional procedure, the surgeon makes a large cut in the groin area. The hernia sac is carefully pushed back into the abdomen, and the weakened abdominal wall is repaired, often reinforced with sutures or a mesh. The cut is then closed with stitches.
2. Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair Surgery:
This minimally invasive technique involves making several small cuts in the abdominal wall. A laparoscope (a thin tube with a light and camera) is inserted through one incision, and surgical instruments are inserted through the others. The surgeon uses the laparoscope to view and repair the hernia, generally using mesh for reinforcement. Laparoscopic surgery results in smaller incisions and a quicker recovery.
Medical Treatments for Inguinal Hernia
Common medications used to manage symptoms include:
1. Pain Relievers:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce discomfort.
2. Antibiotics:
If the inguinal hernia becomes infected, a surgeon may prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection.
3. Medications to Relieve Constipation:
To avoid straining during bowel movements, which can worsen hernia symptoms, stool softeners or laxatives may be recommended to prevent constipation.
Non-surgical Treatment for Inguinal Hernia
An inguinal hernia normally does not go away without surgical intervention. However, non-surgical approaches like lifestyle modifications can ease pain and discomfort. Surgery, on the other hand, can effectively treat inguinal hernia and prevent the risk of other complications like bowel obstruction. Some of the non-surgical treatments for inguinal hernia area are as follows:
1. Management of weight and diet:
By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce the pressure on the abdomen. Doctors also encourage patients to consume a fibre-rich diet to avoid straining during bowel movements.
2. Limiting strenuous activities:
Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities that increase abdominal pressure. Instead, focus on exercises that strengthen your core muscles. Recommended exercises include inclined leg lifts, inclined cycling and pillow squeezes to strengthen the muscles of the abdomen.
3. Changing bowel habits:
Avoid straining during bowel movement, as it can cause further discomfort.
4. Maintaining proper posture:
It is essential that you maintain proper posture as improper posture can strain the abdominal muscles.
5. Applying ice:
If you experience swelling, redness or pain sensation in the groin or abdomen area, consider applying ice to the inflamed area to gain some relief.
Most suitable surgery for Inguinal Hernia Treatment
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair has become the preferred method for several important reasons:
- This minimally invasive technique uses smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery, leading to less pain after surgery and faster recovery for patients.
- Laparoscopy’s improved visualisation allows surgeons to identify and repair multiple hernias in one procedure, making it especially useful for treating recurrent hernias.
- Smaller incisions also reduce the risk of infection and patients often experience less scarring from the procedure.
- Additionally, the minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic surgery lowers the risk of complications, such as blood loss.
These factors make laparoscopic surgery the preferred choice among surgeons for inguinal hernia treatment.
Preparation Tips For Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Surgery
Preparing for laparoscopic inguinal hernia surgery involves the following steps:
1. Consult with the Surgeon:
Discuss the procedure, anaesthesia options, and any questions or concerns you may have. Your surgeon will provide detailed guidance.
2. Preoperative Tests:
The surgeon may order preoperative tests, such as blood tests and an ECG, to check your health.
3. Medication:
Inform the surgeon about all medications and supplements. They may recommend adjusting or discontinuing certain medications before the surgery.
4. Fasting Instructions:
Generally, you should not eat or drink anything for several hours before the surgery. Follow the surgeon’s fasting instructions carefully.
5. Transportation Arrangements:
Ensure you have someone to drive you to and from the hospital on the day of the procedure.
6. Comfortable Clothing:
Bring loose-fitting, comfortable clothing to wear after the surgery.
7. Diet Considerations:
Maintain a balanced diet in the days leading up to the surgery, and avoid heavy or spicy meals the night before.
8. Smoking and Alcohol:
If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing your intake before the surgery, as smoking can affect healing. Avoid alcohol in the days leading up to the procedure.
9. Post-operative Care Discussion:
Discuss with our inguinal hernia doctor regarding post-operative care, pain management, and any activity restrictions during the recovery period. You may need to take it easy and avoid certain activities as you heal.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Surgery
Surgical treatment for inguinal hernia offers several key benefits:
Prevention of Complications:
If left untreated, inguinal hernias can lead to serious issues like incarceration (when the hernia cannot be pushed back) and strangulation (cutting off blood supply to the herniated tissue), both of which are medical emergencies. Timely surgery helps prevent these potentially life-threatening situations.
Relief from Discomfort:
Inguinal hernias can cause pain, discomfort, and a noticeable bulge in the groin. Surgical repair relieves these symptoms, significantly improving your well-being.
Decreased Risk of Recurrence:
Advances in surgical techniques, particularly the use of mesh, have significantly reduced the likelihood of hernia recurrence. These modern methods offer excellent long-term success rates.
Prevention of Hernia Enlargement:
Inguinal hernias tend to worsen over time if left untreated. Surgery prevents the hernia from enlarging and becoming more difficult to repair.
Improved Mobility:
After surgery, the strengthened abdominal wall allows you to resume daily activities and physical tasks more comfortably, improving your mobility.
Reduced Blood Loss:
Another advantage of laparoscopic inguinal hernia surgery is reduced blood loss compared to traditional open surgery. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure, involving smaller incisions and precise surgical instruments, allows surgeons to repair the hernia with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues, lowering the risk of bleeding during the operation.
Better Quality of Life:
By addressing both the hernia and its potential complications, surgical treatment can significantly improve the quality of life, enabling you to live without the limitations caused by the hernia.
Recovery Guidelines After Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Surgery
Here are some recovery tips to keep in mind:
1. Prioritise Rest:
In the first few days after your inguinal hernia repair surgery, rest is crucial. Avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities, and vigorous exercise for at least 4 to 6 weeks.
2. Manage Pain:
You may experience some pain and discomfort post-surgery. Follow the surgeon's advice on prescribed pain medications.
3. Wound Care:
Keep the surgical incision clean and dry. Adhere to the surgeon’s instructions regarding wound care and bandage changes.
4. Diet Progression:
Start with clear liquids and gradually reintroduce solid foods to your diet. Staying hydrated is essential for your recovery.
5. Prevent Constipation:
Pain medications and decreased physical activity can lead to constipation. Eat high-fibre foods for smooth bowel movements.
6. Follow-Up Appointments:
Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor your healing progress.
7. Gradual Activity Increase:
After the initial healing phase, slowly reintroduce light activities and increase your mobility.
8. Monitor for Issues:
Be aware of signs of infection (such as redness, swelling, or fever), hernia recurrence, or any unusual symptoms. Contact the doctor if you notice any problems.
Cost of Inguinal Hernia Surgery in Kolkata
Several factors can influence the cost of inguinal hernia surgery in Kolkata. Here are some key considerations:
1. Type of Hospital:
The choice of hospital plays a significant role in determining costs.
2. Surgeon’s Fee:
The experience and reputation of the surgeon can also impact the overall cost of inguinal hernia surgery.
3. Surgical Method:
The type of surgery performed—open or laparoscopic—can affect the cost.
4. Anaesthesia Type:
The choice of anaesthesia can influence costs as well. General anaesthesia is usually more expensive than local or regional anaesthesia.
5. Length of Hospital Stay:
The duration of your hospital stay after the surgery can affect the total cost. Laparoscopic procedures often result in shorter hospital stays compared to open surgeries.
Our Patient Love Us
Get in Touch
Tell us about your disease and Dactar Babu will get the best treatment option for you.


3.png)






